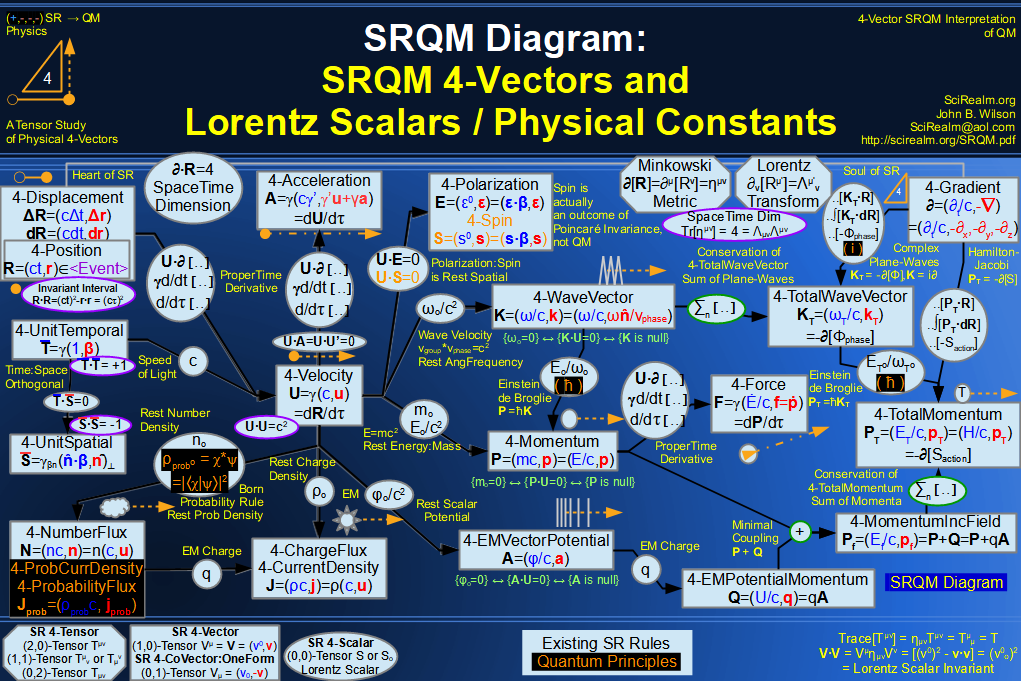
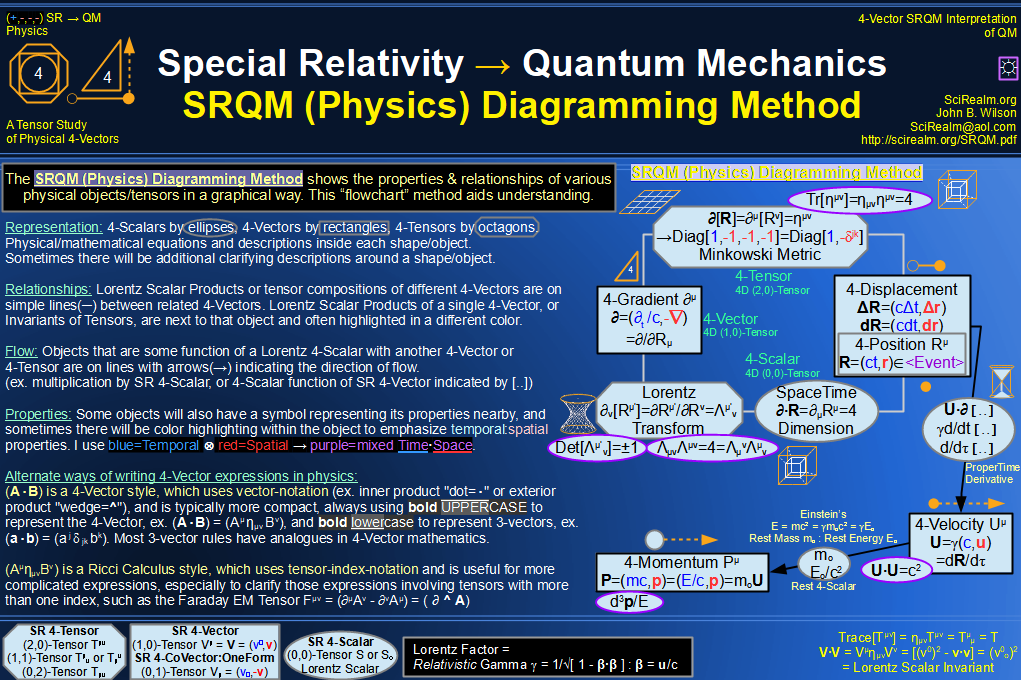
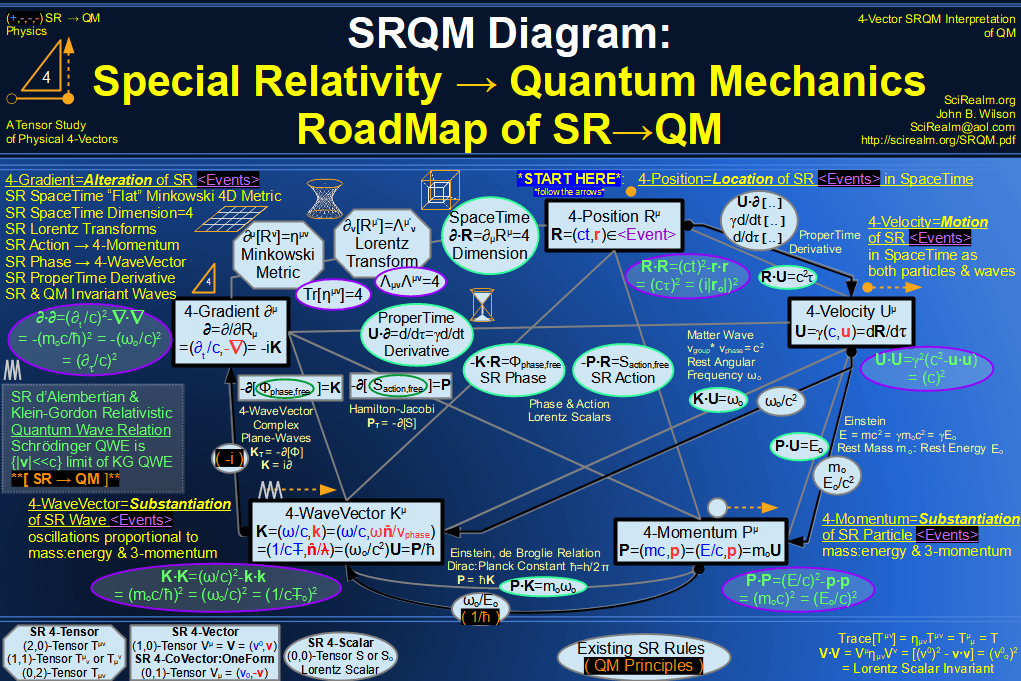
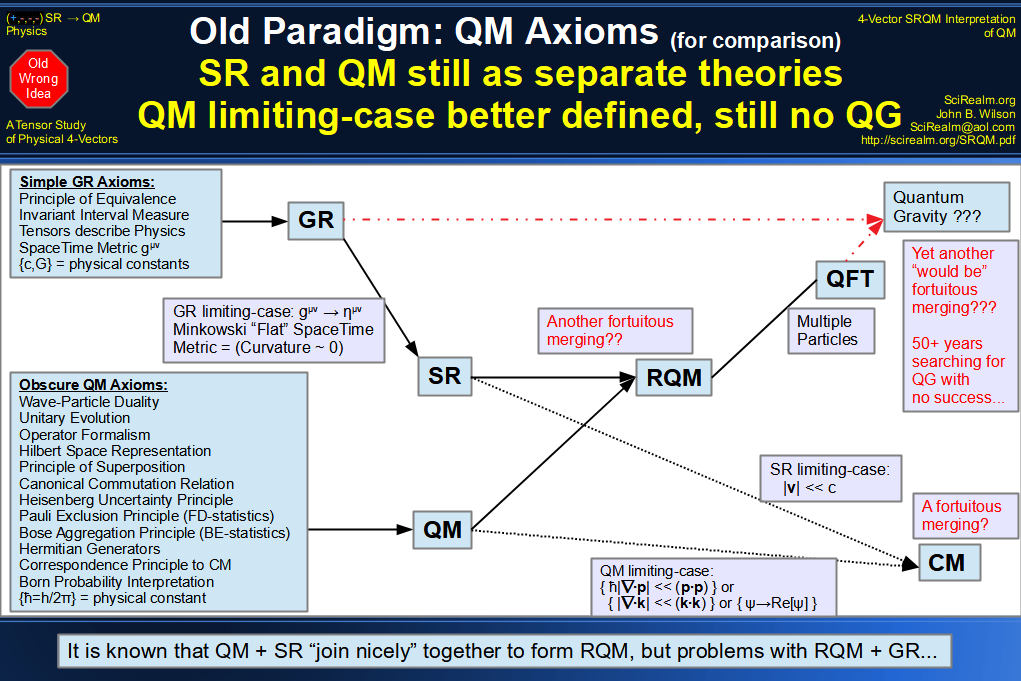
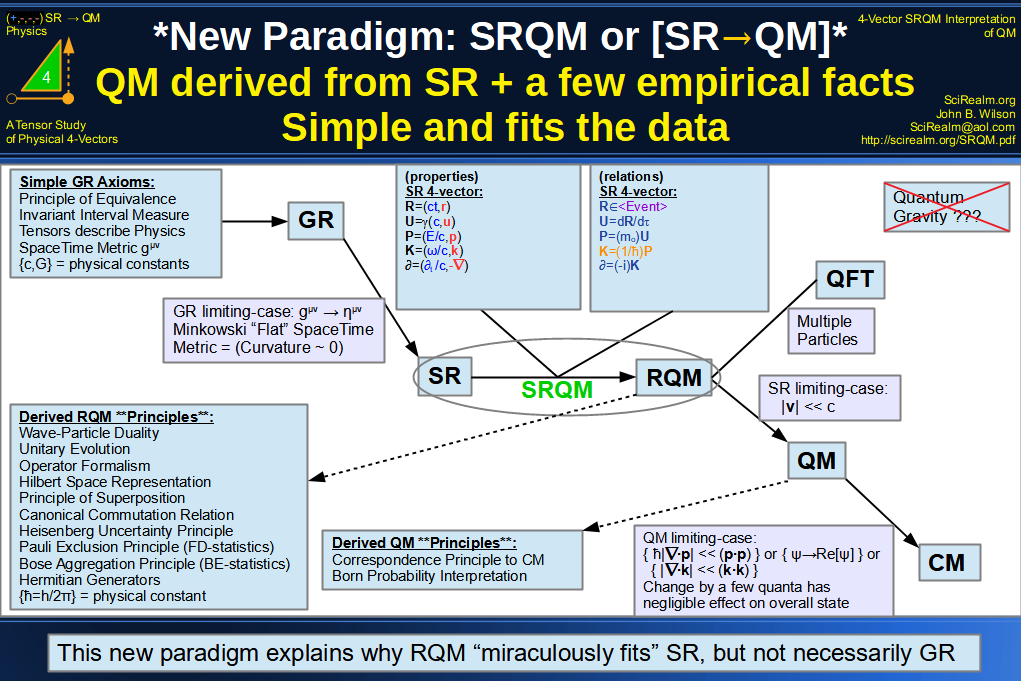
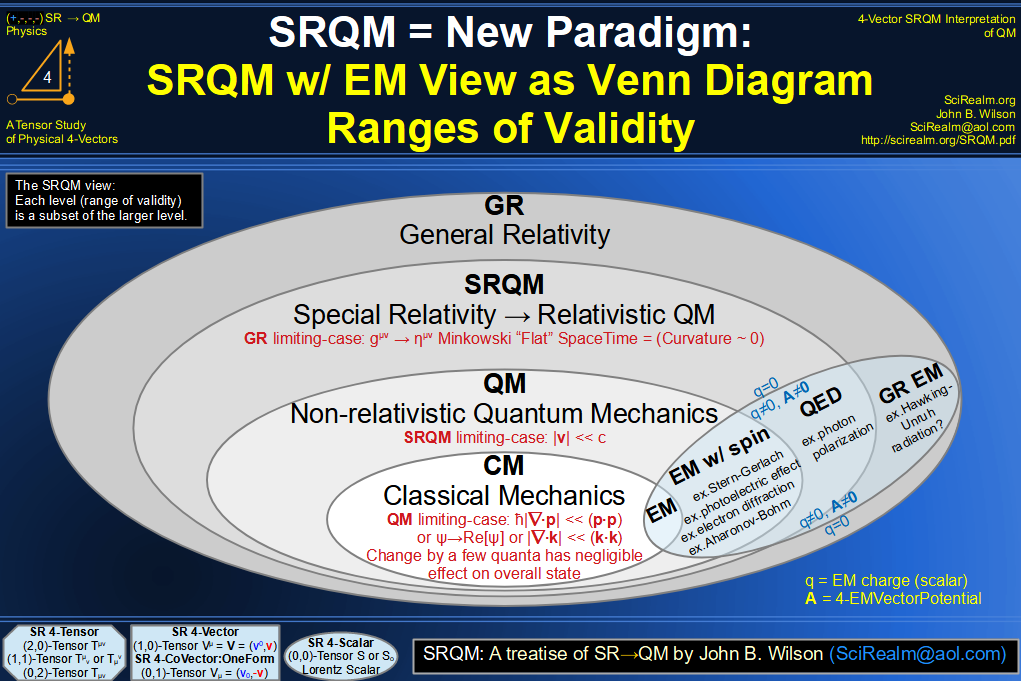
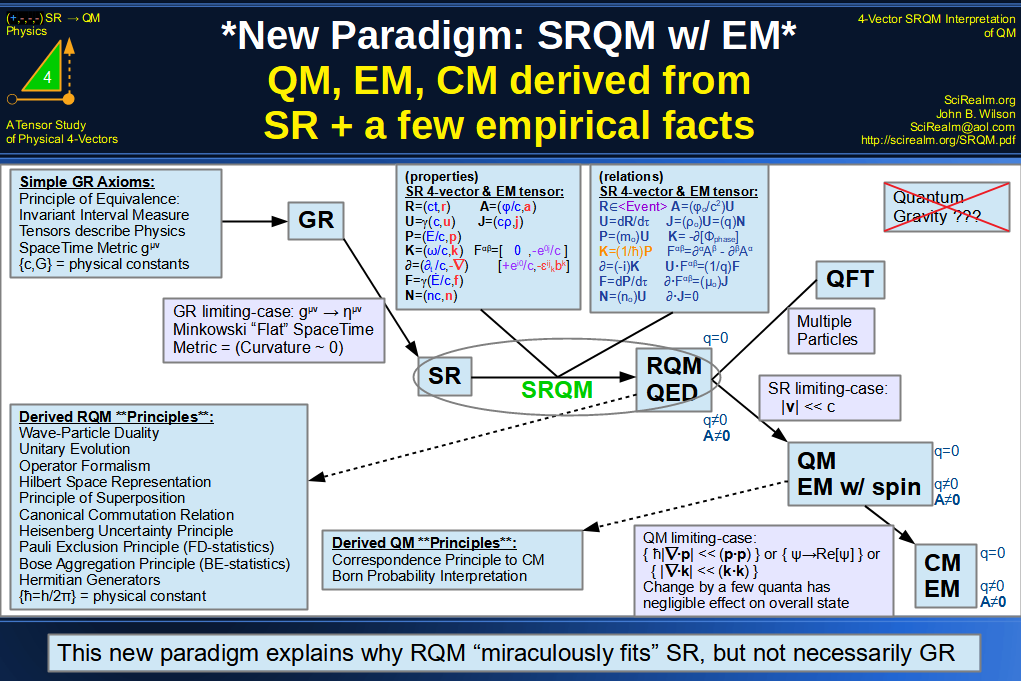
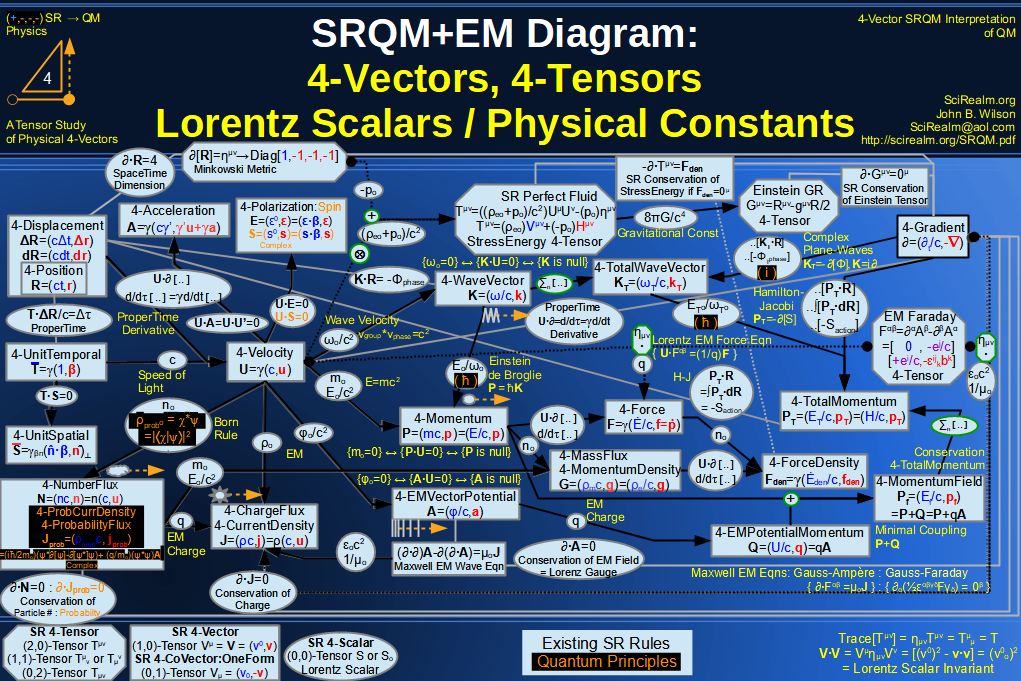
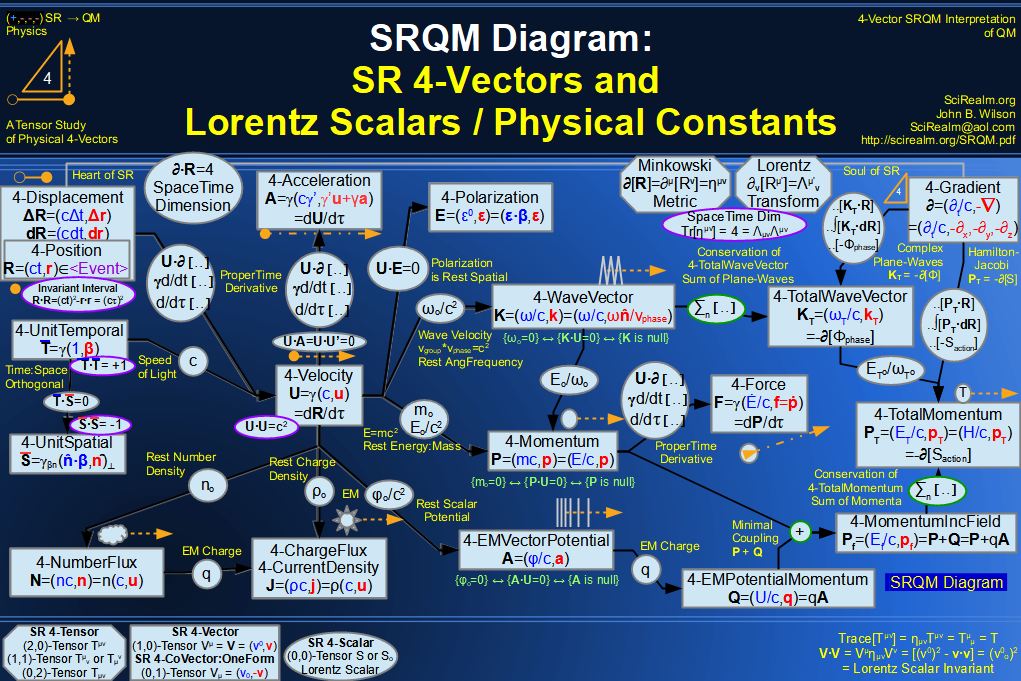
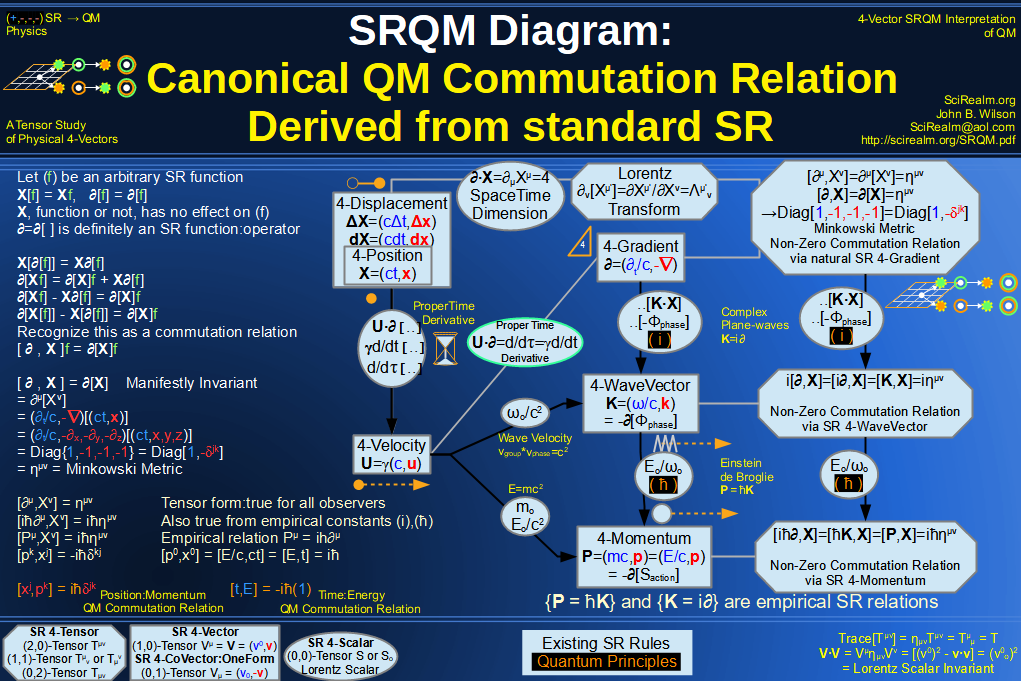
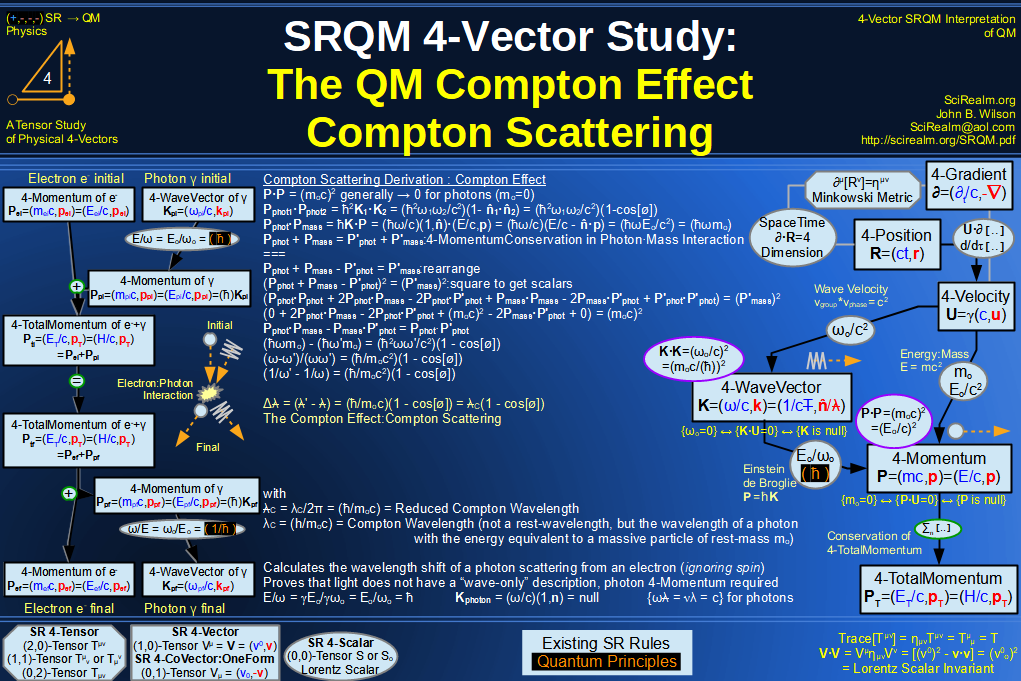
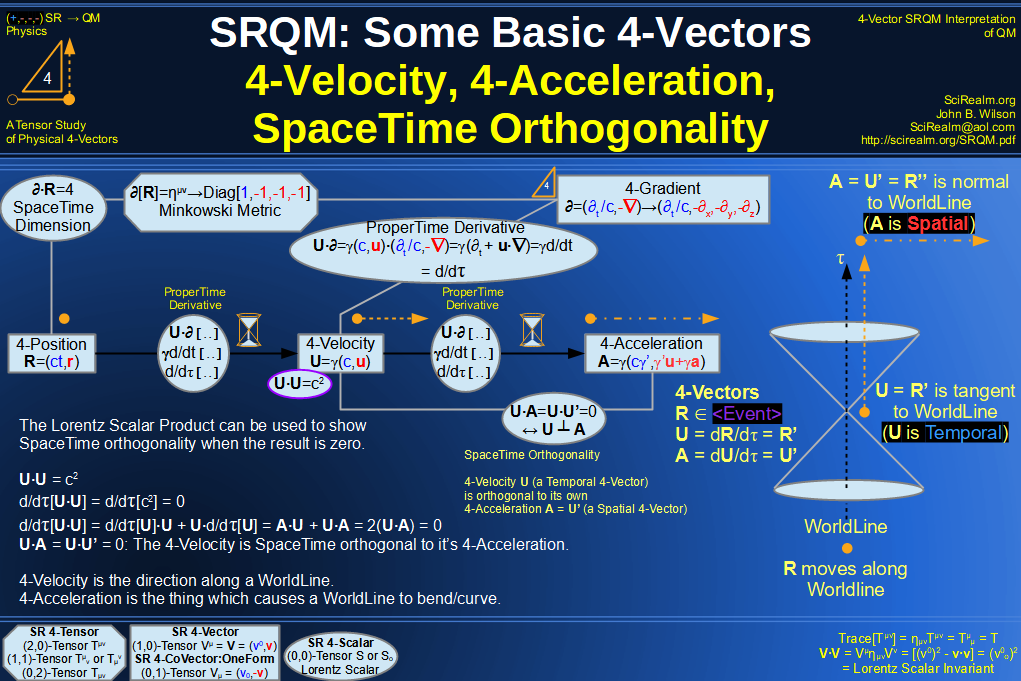
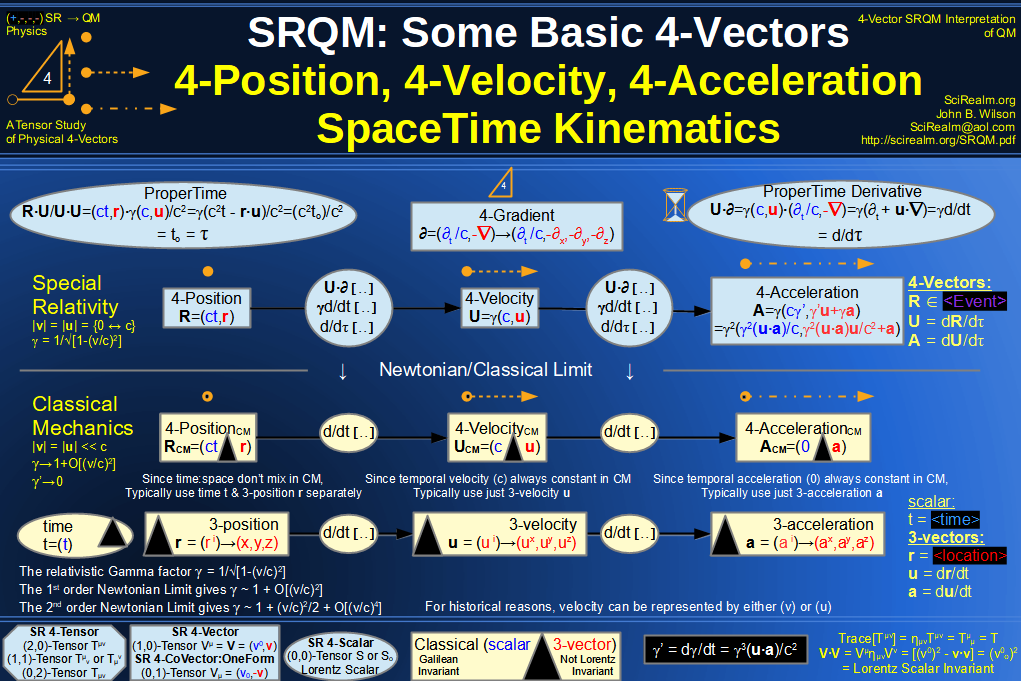
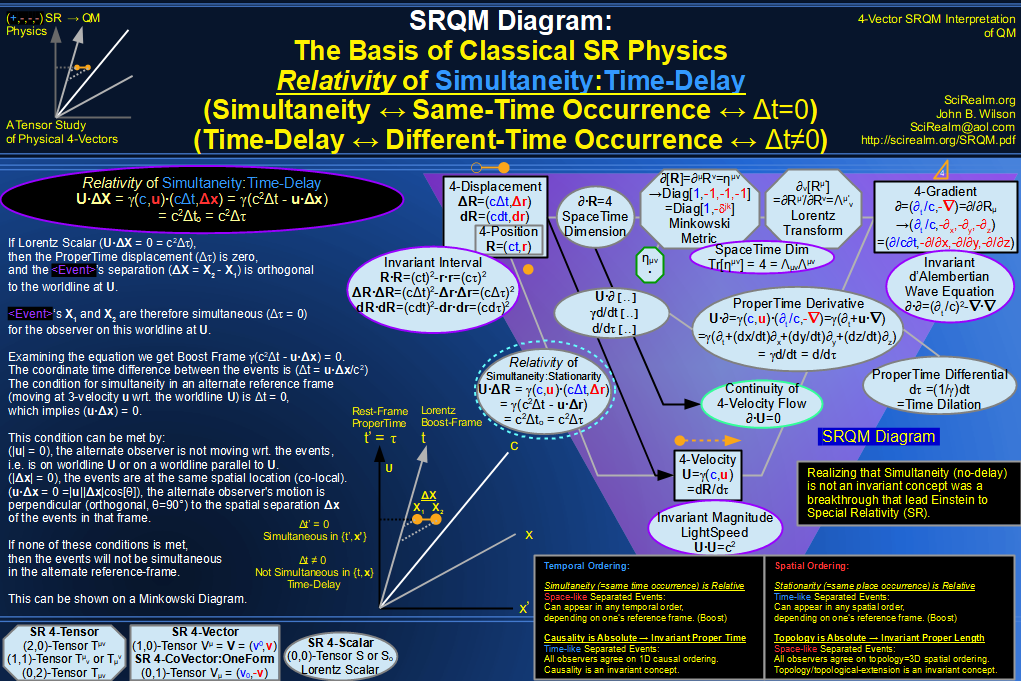
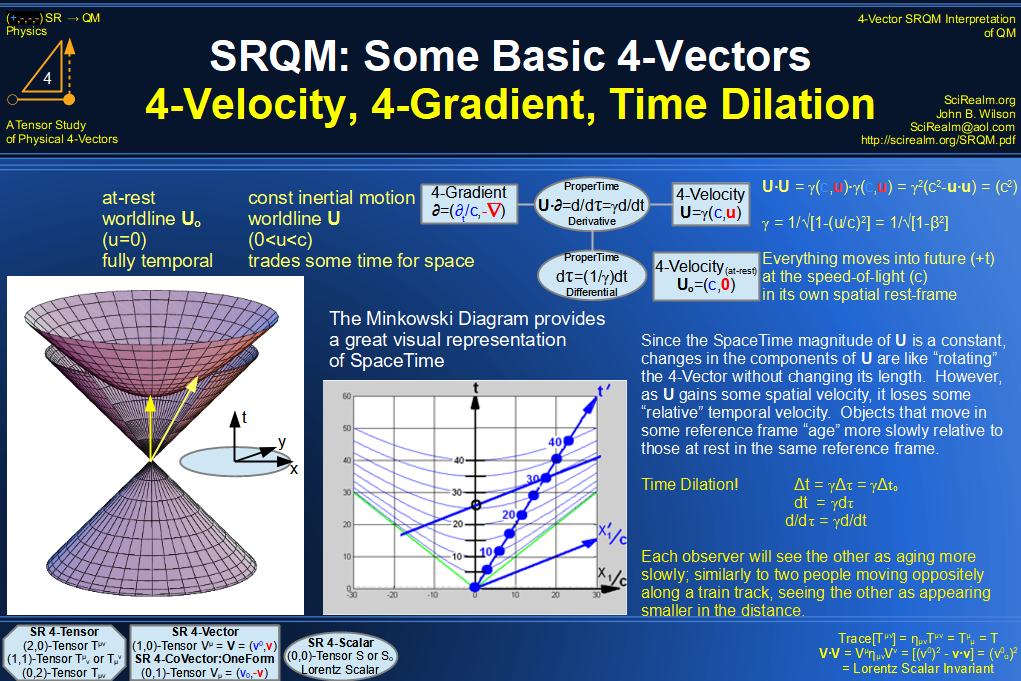
| Wave Type: |
Scalar Waves |
Photonic/EM Waves (4-Vectors) |
Gravitational Waves (2,0)-Tensors |
Lanczos Potential Tensor
Gravitational Waves |
| Special Background Conditions: |
None |
None |
Linearized Gravity = Weak Field limit
gμν = ημν + hμν
where |hμν| << 1
Minkowski SpaceTime limit
hμν acts like Tensor Field propagating
in "flat" Minkowski SR |
SR |
| Field Type: |
(0,0)-Tensor
= Scalar |
(1,0)-Tensor
= 4-Vector |
(2,0)-Tensor |
(3,0)-Tensor |
| Field Identifier: |
Φ |
A = Aμ |
hTTμν |
Hμνρ or Lμνρ |
| Special Tensor Conditions: |
|
None, 4 possible independent components.
Lorentz Invariant Conditions
will reduce # of independent component. |
(hTTμν) = (hTTνμ)
hTTμν = hTT(μν)
Symmetric 2-Tensor
----
Reduces independent components
from 16 down to 10
Other Lorentz Invariant Conditions
will reduce it further |
Lμνρ + Lνμρ = 0
Lμνρ = L[μν]ρ
AntiSymmetric on first 2 indices
Lμνρ + Lρμν + Lνρμ = 0
L[μνρ] = 0
Jacobi/Bianchi Identity
----
Reduces independent components
from 64 down to 20
Other Lorentz Invariant Conditions
will reduce it further |
Conservative Field Condition:
4-Divergence = 0
4-Divergenceless = Lorenz Gauge
Carroll also uses Lorenz Gauge for gravitational wave
in Intro to GR: SpaceTime and Geometry, pg. 301
Other names include:
Harmonic Gauge
Einstein Gauge
Hilbert Gauge
de Donder Gauge
Fock Gauge |
N/A |
(∂·A) = (∂μAμ) = 0
A is conserved |
(∂·hTTμν)
= (∂νhTTμν)
= (hTTμν,ν)
= 0μ
hTTμν is conserved |
Lanczos differential gauge SR
(∂·Lμνρ)
= (∂ρLμνρ)
= Lμνρ,ρ
= 0μν |
Purely Spatial Wave Condition:
Orthogonal to 4-Velocity U |
|
(U·A) = (UνAν) = 0 for a photonic wave
Generally
AEM·U = (φ/c,a)·γ(c,u) = γ(φ - a·u) = φo
As we will see, this is a photonic wave and the
rest potential φo will be zero in the same way that
the rest mass mo of a photon is zero
In other words:
There is no "at-rest" frame for light-like
(U·A) = 0 = γ(c,u)·(φ/c,a) = γ[φ - u·a] = 0
Therefore, φ = u·a
Therefore A = (u·a/c,a)
To an at-rest observer (u=0), A appears spatial A → (0,a)
To an â-null observer (u=câ), A appears null A → (|a|,a)
A 3rd situation is that u·a=0 via 3D orthogonality,
in which case A appears spatial A → (0,a) |
(U·hTTμν) = (UνhTTμν) = 0μ |
|
Traceless Condition:
Equivalent to Null = Photonic Condition: |
|
Generally
A·A = (AμημνAν) = (φ/c,a)·(φ/c,a) = (φ/c)2 - a·a
From above, A = (u·a/c,a)
A·A = (u·a/c,a)·(u·a/c,a) = [(u·a/c)2 - a·a)]
To an at-rest observer (u=0), A·A = (- a·a) appears spatial
To an â-null observer (u=câ), A·A = (0) appears null
A 3rd situation is that u·a=0 via 3D orthogonality,
in which case A appears spatial A → (0,a)
and A·A = (- a·a) appears spatial |
Tr[ hTTμν ] = (ημνhTTμν) = hTTνν = 0 |
Lanczos algebraic gauge SR
Tr[ Lμνρ ]
= (ηνρLμνρ)
= ( Lμρρ)
= 0μ |
Transverse Condition:
Occurs due to the combination of:
Solution is Free Plane Wave: gives K·K = 0, K is null
The Conservative Field Condition: gives K·C = 0
The Purely Spatial Condition: gives Uo·C = 0
The combination leads to the spatial k·c = 0
The wave is transverse |
|
|
The Transverse-Traceless Gauge (TT)
aka. the Radiation Gauge |
|
| Wave Equation with Source: |
|
(∂·∂)Aν = μo Jν |
(∂·∂)hTTμν = -2 Gμν
(∂·∂)hTTμν = -16πG Tμν
I'm not sure about the signs
Also, this is linerized approx to GR |
complicated |
Wave Equation without Source:
ie. Freely-propagating |
(∂·∂)Φ = 0 |
(∂·∂)Aν = 0ν |
(∂·∂)hTTμν = 0μν |
(∂·∂)Lμνρ = 0μνρ |
Free Wave Solution:
Plane Wave with C or Cν or Cμν or Cμνρ
as respective wave amplitudes |
Φ = C e(iK·X) |
Aμ = Cμ e(iK·X) |
hTTμν = Cμν e(iK·X) |
Lμνρ = Cμνρ e(iK·X) |
Solution Check:
assumes that the wave amplitude C... is a constant |
(∂·∂)Φ
= ηρσ ∂ρ∂σ C e(iK·X)
= i ηρσ ∂ρKσ C e(iK·X)
= i2 ηρσ KρKσ C e(iK·X)
= - KσKσ Φ
= 0 |
(∂·∂)Aμ
= ηρσ ∂ρ∂σ Cμ e(iK·X)
= i ηρσ ∂ρKσ Cμ e(iK·X)
= i2 ηρσ KρKσ Cμ e(iK·X)
= - KσKσ Aμ
= 0ν
|
(∂·∂)hTTμν
= ηρσ ∂ρ∂σ Cμν e(iK·X)
= i ηρσ ∂ρKσ Cμν e(iK·X)
= i2 ηρσ KρKσ Cμν e(iK·X)
= - KσKσ hTTμν
= 0μν |
(∂·∂)Lμνρ
= ηρσ ∂ρ∂σ Cμνρ e(iK·X)
= i ηρσ ∂ρKσ Cμνρ e(iK·X)
= i2 ηρσ KρKσ Cμνρ e(iK·X)
= - KσKσ Lμνρ
= 0μνρ |
| Trivial Solution = No Wave = (Field = 0) |
Φ = 0 |
Aμ = 0μ |
hTTμν = 0μν |
Lμνρ = 0μνρ |
Interesting Solution = Wave
4-WaveVector K is Null
Massless = LightLike = Photonic |
KσKσ = 0 |
KσKσ = 0 |
KσKσ = 0 |
KσKσ = 0 |
4-Divergenceless Check
4-WaveVector K orthogonal to 4-WaveAmplitude C...
4-WaveVector K orthogonal to 4-Polarization E
4-WaveVector K orthogonal to Polarization Tensor |
|
(∂·A) = (∂μAμ) = 0
∂μCμ e(iK·X) = 0
iKμCμ e(iK·X) = 0
KμCμ = 0 |
(∂·hTTμν) = (∂νhTTμν) = 0μ
∂νCμν e(iK·X) = 0μ
iKνCμν e(iK·X) = 0μ
KνCμν = 0μ |
(∂·Lμνρ) = (∂ρLμνρ) = 0μν
∂ρCμνρ e(iK·X) = 0μν
iKρCμνρ e(iK·X) = 0μν
KρCμνρ = 0μν |
Examine Solutions:
general null K = (ω/c) (1,n̂)
assume null K = (ω/c,0,0,ω/c) in spatial z-direction |
C |
C = Cν =
→ (0,c1,c2,0) |
Cμν =
→
| 0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 0 |
c11 |
c12 |
0 |
| 0 |
c12 |
-c11 |
0 |
| 0 |
0 |
0 |
0 | =
| 0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 0 |
h+ |
hx |
0 |
| 0 |
hx |
-h+ |
0 |
| 0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Cμνρ =
→... |
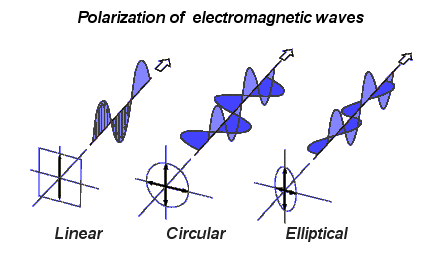
Find Polarizations:
**Note**
The 4-Polarization E = Cν
The Polarization Tensor Cμν
both can have complex components.
These give circular and elliptical polarizations
Circular/elliptical polarizations should also
carry angular momentum |
Non-polarized |
→ (0,c1,c2,0)
→ (0,cx,cy,0)
→ (0,1,0,0) = x-polarized
→ (0,0,1,0) = y-polarized (rotated 90°)
for photon travelling in z-direction
using the Jones Vector formalism n = z / |z|
and to the observer at rest
C = (0,1,0,0) : x-polarized linear
C = (0,0,1,0) : y-polarized linear
C = √[1/2] (0,1,1,0) : 45° from x-polarized linear
C = √[1/2] (0,1,i,0) : right-polarized circular
C = √[1/2] (0,1,-i,0) : left-polarized circular
General-polarized (elliptical) for z-photon
C = (0,Cos[θ]Exp[iαx],Sin[θ]Exp[iαy]),0)
C* = (0,Cos[θ]Exp[-iαx],Sin[θ]Exp[-iαy]),0)
|
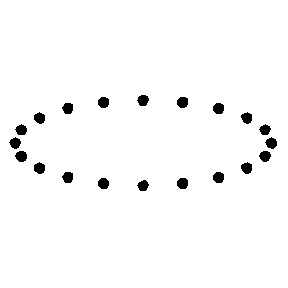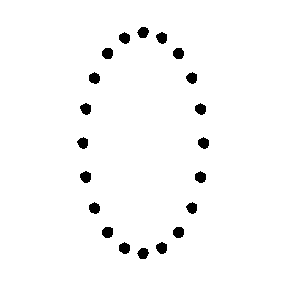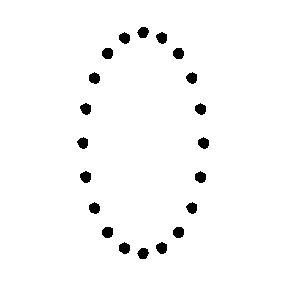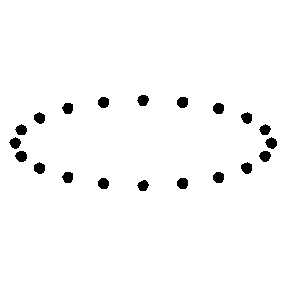
h+ = plus pattern
hx = cross pattern (rotated 45°)
hR = (1/√2)(h+ + ihx) = Right Circular
hL = (1/√2)(h+ - ihx) = Left Circular
etc.
Presumably there could be
Elliptical polarizations for grav-waves
also
Test Particle Masses:
Plus (+) Polarization
Cross (x) Polarization
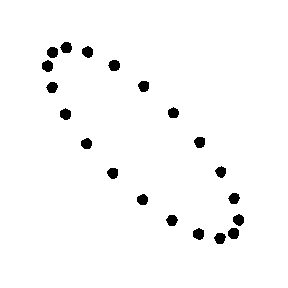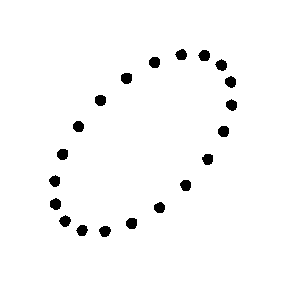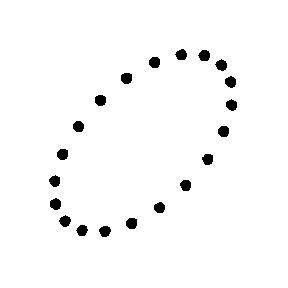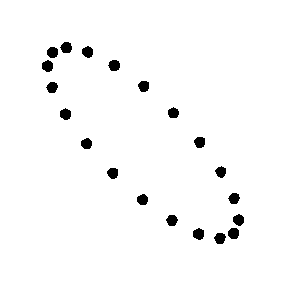 | ... |